A growing and dividing cell goes through a series of stages called the cell cycle. During this phase the cell grows makes a copy of its DNA the chromosomes are copied and prepares to divide into two cells.

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation Teachmephysiology
There are two main stages in the cell cycle of a typical eukaryotic somatic cell.

. Interphase mitosis cytokinesis g1 phase g2 phase synthesis phase prophase metaphase anaphase telophase. The mitotic phase begins with karyokinesis mitosis which consists of five stages. Growth Phase where normal cellular processes take place and the cell grows to full size.
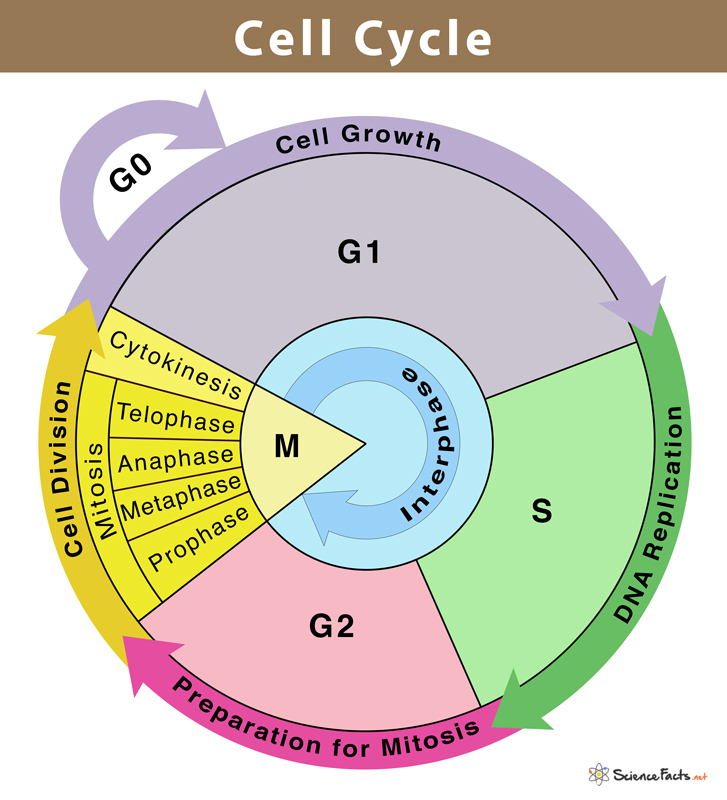
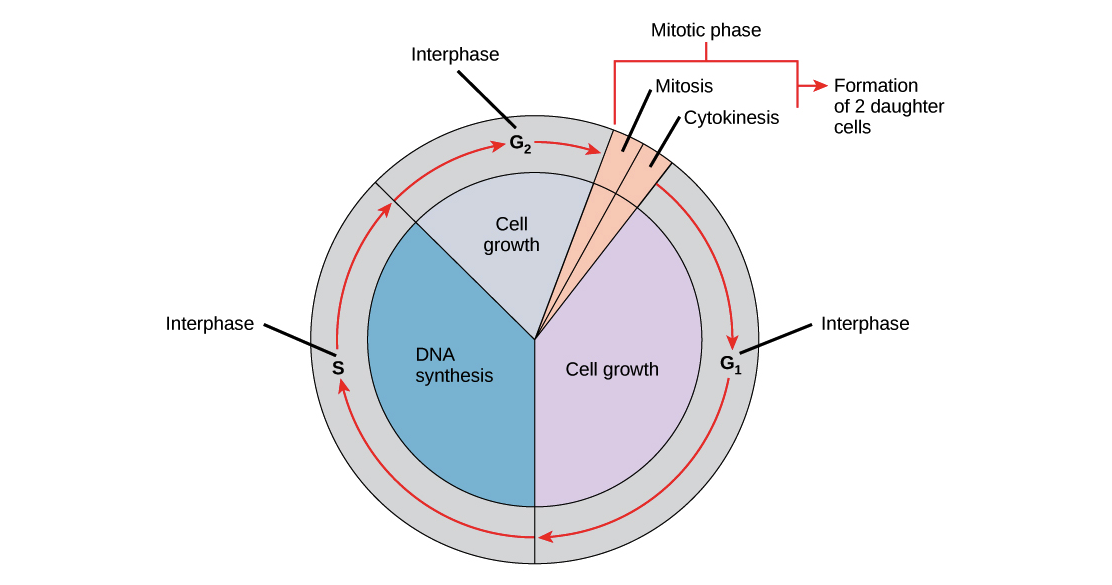
Stages G1 S and G2 must always occur in this order. The five stages of cell cycle are interphase which is in turn classified into G1 S and G2 phase Mitosis also called as the M phase which is further divided into 4 parts prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase and Cytokinesis. Interphase is the resting stage of a cell.
S synthesis phase 3. The cell cycle contains six main stages. The following points highlight the four major phases of the cell cycle.
The cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. G1 is the stage where the cell is preparing to divide. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages.
Interphase occurs prior to the beginning of mitosis and encompasses whats called stage G1 or first gap stage S or synthesis and stage G2 or second gap. The cell cycle is a 4-stage process consisting of Gap 1 G1 synthesis S Gap 2 G2 and mitosis M which a cell undergoes as it grows and divides. G 1 gap1 phase 2.
To do this it then moves into the S phase where the cell copies all the DNA. The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth then synthesis of DNA. A shorter phase of nuclear division.
So S stands for DNA synthesis. Interphase where the DNA is replicated. The phases in the reproduction and growth of a cell is known as the cell cycle.
Phases of the Cell Cycle. The stages of the cell cycle in order are interphase prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events.
Cell grows performs its normal functions and prepares for division. Terms in this set 11 Interphase. The different phases of a cell cycle include.
From G0 the cell can undergo terminal differentiation. This process is known as mitosis and is used to generate new cells. Interphase is divided into G 1 S and G 2 phases.
M phase This is the mitotic phase and is divided into prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. The two structures that are being copied are cylindrical in shape and are called centrioles. Mitotic phase or M-phase.
It is sometimes referred to as the cell division cycle for that reason. G 2 gap 2 phase 4. Cell cycle the ordered sequence of events that occur in a cell in preparation for cell division.
Mitosis where the nucleus divides and sister chromatids are separated. Cell cycle is the name we give the process through which cells replicate and make two new cells. This is the first stage of the cell cycle and occurs before mitosis.
It is characterised by a change in the chromosome from the condensed mitotic state to the more extended interphase. Stages of the cell cycle. Cell cycle has different stages called G1 S G2 and M.
The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size gap 1 or G1 stage copies its DNA synthesis or S stage prepares to divide gap 2 or G2 stage and divides mitosis or M stage. After completing the cycle the cell either starts the process again from G1 or exits the cycle through G0. Consists of G1 S.
New cells are born through the division of their parent cell producing two daughter cells from one single parent cell. The G 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. The cell cycle begins with stage G1 which is a part of interphase.
Interphase This phase includes the G1 phase S phase and the G2 phase. Phases of cell cycle. The cell cycle proper is split into.
In eukaryotes the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period called interphase. The stages G1 S and G2 make up interphase which accounts for the span between. The replication of DNA occurs during the S phase of this stage.
A long non-dividing state also known as inter-mitosis or I-phase. So how does the parent cell prep itself for mitosis during interphase.
0 Comments